What is the Difference Between PA6 and PP?
December 2, 2024
What is a FR4 sheet?
December 3, 2024Polycarbonates (PC) are a group of thermoplastic polymers known for their high impact resistance, optical clarity, and heat resistance. They are made from the polymerization of bisphenol A (BPA) and phosgene. Polycarbonates are widely used in various industries, including automotive, electronics, construction, and medical, due to their versatile properties.
Key Properties of Polycarbonates
Polycarbonates are renowned for their excellent mechanical strength, durability, and transparency. They are highly resistant to impact and can withstand significant physical stress without cracking or breaking, making them ideal for applications where safety is critical. Additionally, polycarbonates are thermally stable and can tolerate moderate temperatures without losing their structural integrity.
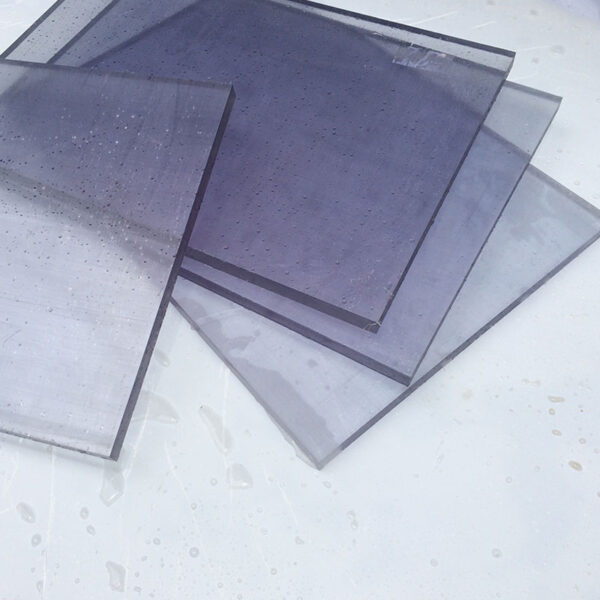
Optical Clarity and Transparency
One of the defining features of polycarbonate is its optical clarity. It is often used in applications where transparency is necessary, such as in eyewear lenses, optical discs (CDs, DVDs), and protective covers. Polycarbonate offers high light transmission, similar to glass, while being much lighter and more durable.
Applications of Polycarbonates
Polycarbonates have a wide range of applications due to their combination of strength, clarity, and heat resistance. They are used in the automotive industry for headlamp lenses, in construction for windows and skylights, and in electronics for housings and screens. Polycarbonates are also used in medical devices, eyewear, and safety equipment like helmets due to their impact resistance.
Environmental Considerations
While polycarbonates offer significant advantages, their production and disposal can raise environmental concerns, particularly due to the use of BPA. However, research into BPA-free alternatives and recycling methods is ongoing to address these concerns.